Acid Site Characterization of H+ Y (SiO2/Al2O3:5.2/1): A Pulse Chemisorption and TPD Application for the AutoChem
The Brønstead acidity of zeolites and other catalysts is of keen interest, as this affects the kinetics of reactions. Characterization of these sites is consequently very important and is often performed according to the ASTM D 4824 ammonia chemisorption method. An alternative, but comparable, characterization method involves pulse chemisorption of propylamines followed by a temperature-programmed […]
Acid Site Characterization of H+ Mordenite (SiO2/Al2O3:90/1): A Pulse Chemisorption and TPD Application for the AutoChem
The Brønstead acidity of zeolites and other catalysts is of keen interest, as this affects the kinetics of reactions. Characterization of these sites is consequently very important and is often performed according to the ASTM D 4824 ammonia chemisorption method. An alternative, but comparable, characterization method involves pulse chemisorption of propylamines followed by a temperature-programmed […]
Acid Site Characterization of H+ β (SiO2/Al2O3:150/1): A Pulse Chemisorption and TPD Application for the AutoChem
The Brønstead acidity of zeolites and other catalysts is of keen interest, as this affects the kinetics of reactions. Characterization of these sites is consequently very important and is often performed according to the ASTM D 4824 ammonia chemisorption method. An alternative, but comparable, characterization method involves pulse chemisorption of propylamines followed by a temperature-programmed […]
Acid Site Characterization of H+ ZSM-5 (SiO2/Al2O3:30/1): A Pulse Chemisorption and TPD Application for the AutoChem
The Brønstead acidity of zeolites and other catalysts is of keen interest, as this affects the kinetics of reactions. Characterization of these sites is consequently very important and is often performed according to the ASTM D 4824 ammonia chemisorption method. An alternative, but comparable, characterization method involves pulse chemisorption of propylamines followed by a temperature-programmed […]
Temperature Programmed Reduction Using the AutoChem
Temperature-programmed reduction (TPR) is a widely used tool for the characterization of metal oxides, mixed metal oxides, and metal oxides dispersed on a support. The TPR method yields quantitative information of the reducibility of the oxide’s surface, as well as the heterogeneity of the reducible surface. TPR is a method in which a reducing gas […]
Accuracy of Vapor Dosing with the AutoChem
The Vapor Generator option for the AutoChem provides a means to quantitatively inject pulsed dose amounts of vapor onto a solid sample. Vapors of most interest are actually gases below their critical temperature; hence, they are condensable. Design features and operation of the AutoChem’s vapor generator are described in Product Bulletin 83. Reagent grade 2-propanol […]
Acid Site Characterization of H+ ß (SiO2/Al2O3:75/1): A Pulse Chemisorption and TPD Application for the AutoChem
The Brønstead acidity of zeolites and other catalysts is of keen interest, as this affects the kinetics of reactions. Characterization of these sites is consequently very important and is often performed according to the ASTM D 4824 ammonia chemisorption method. An alternative, but comparable, characterization method involves pulse chemisorption of propylamines followed by a temperature-programmed […]
An Introduction to Chemical Adsorption Analytical Techniques and Methods (Condensed Version)
Author: Paul A. Webb This article is a condensed version of a more comprehensive article titled “Chemical Adsorption,” as an Analytical Technique. Introduction Catalysts are used in a variety of applications from the production of consumer goods to the pro-tection of the environment. Optimum design and efficient utilization of catalysts requires a thor-ough understanding of […]
Autochem III – Catalyst and Active Surface Characterization
The AutoChem from Micromeritics is the most widely used and highly cited system for catalyst reactivity characterization because it is also the most automated, highly accurate system for chemisorption and temperature-programmed reactions. The all-new AutoChem III meets and exceeds that performance with a design that will save you hours a day, make the most sensitive, […]
Ammonia TPD for Heat Sensitive Materials on the Autochem III
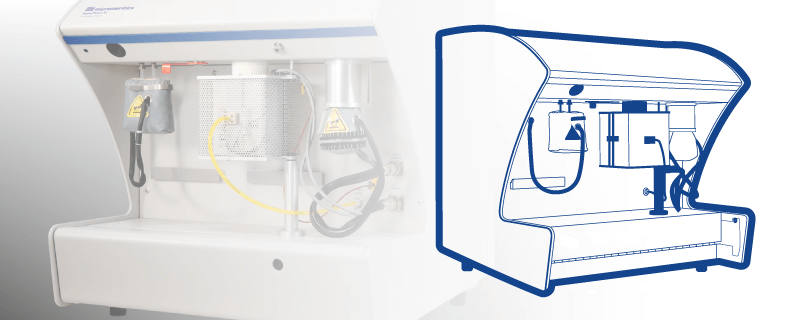
Introduction Zeolites are extensively used in many applications as ion exchange agents, adsorbents, and catalysts. Characterizing the acidity of a zeolite is important to design and optimize it for a catalytic activity of interest. Among many methods developed for characterizing the acid sites of a zeolite, the Temperature Programmed Desorption technique is one of the […]