At Micromeritics, we provide precision instruments tailored for accurate gas adsorption analysis, essential for applications in material science, catalysis, and other advanced fields. This page offers insights into the principles of gas adsorption, the innovative technologies we employ, and how our instruments can enhance your research and industrial applications.
Micromeritics instruments are finely calibrated to measure pressure and temperature which are used to determine the volume of gas adsorbed onto the sample. Data is collected in the form of isotherms, typically from low pressure (~0.00001 torr) to saturation pressure (~760 torr). The pressure range is determined based on the information desired.
The data obtained from physisorption experiments is used to detemine the specific surface area (BET), porosity, and the adsorption capacity of the material.
The amount of gas adsorbed on the materials surface can be used to calculate the surface area. Surface area is a measure of the exposed surface of a solid sample on the molecular scale.
BET (Brunauer, Emmet, and Teller) theory is the most popular model used to determine the specific surface area.
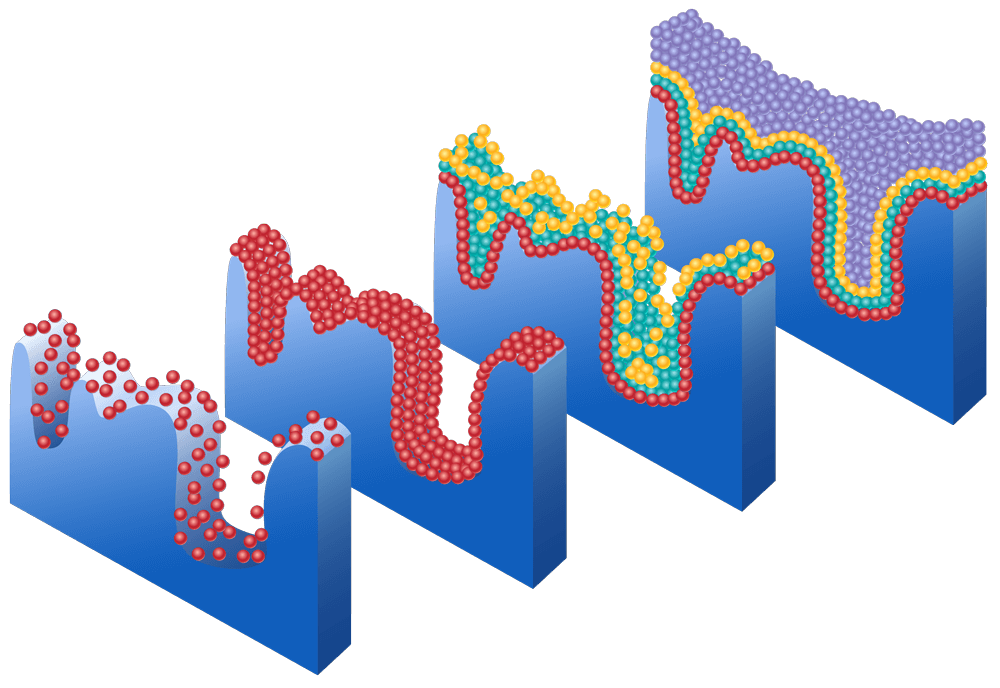
Typically, BET analysis is performed using nitrogen gas (N2) as the adsorbate due to its high affinity for solid surfaces. The gas is introduced at low pressures and molecules begin adsorbing to the surface, as gas pressure increases the monolayer is formed, followed by multilayer adsorption (we have image showing this process). The amount adsorbed is determined to calculate the surface area using the BET equation. For low surface area materials, krypton is commonly used as an alternative adsorbate. Due to its lower vapor pressure (2.5 mmHg) compared to N2 (760 mmHg) at 77.35 K, Kr analyses involve a greater pressure change during the adsorption step at the same relative pressure, resulting in greater accuracy.
| Classification | Size | Typical Calculation Models |
|---|---|---|
| Micropore | < 2 nm | Density Functional Theory (DFT) M-P Method Dubinin Plots (D-R, D-A) Horvath Kawazoe (H-K) t-plot (total micropore area) |
| Mesopore | 2-50 nm | Barrett, Joyner, and Halenda (BJH) Density Functional Theory (DFT) Dollimore-Heal (DH) |
| Macropore | > 50 nm | Barrett, Joyner, and Halenda (BJH) Density Functional Theory (DFT) Dollimore-Heal (DH) |
| *Special Considerations | > 400 nm | For pores exceeding 400 nm, other techniques such as mercury intrusion porosimetry (link to page) are employed. This technique offers insights into larger pores, typically starting from 3 nm up to 1100 µm |

Static chemisorption and dynamic temperature-programmed reactions available





We provide a comprehensive range of characterization services whether it is the analysis of a single sample, a complex method development or validation, new product assessments, or addressing large-scale manufacturing projects.
| Physisorption (Physical Adsorption) | Chemisorption (Chemical Adsorption) |
|---|---|
| Non-selective | Selective |
| Weak Interactions (van der Waals) | Strong Interactions (chemical bonds) |
| Lower Energy | Higher Energy |
| Reversible | Irreversible & Reversible |