A gas pycnometer determines the volume of a material by measuring the pressure change of an inert gas within two calibrated volumes. Density is calculated from the measured volume along with the mass of the sample.
Prior to analyzing, the gas pycnometer purges the sample with an inert gas to clean atmospheric gases, such as water and carbon dioxide, from the material. However, porous materials often require external preparation in order to obtain a clean sample.
Heating a material provides energy to molecules within pores, allowing them to transition into the gas phase. The addition of a vacuum system provides a method in removing molecules as they outgas. When the cleaning process is complete, the sample should be backfilled with an inert gas that does not interact with the sample material.
To demonstrate the impact of pretreatment, 13X, a microporous zeolite, was tested with and without external preparation. The prepared sample was heated at 90°C for one hour, then 350°C for eight hours. Both samples were tested on a 1 cm3 AccuPyc II 1345 using the same instrument parameters. Results are displayed in Table 1.
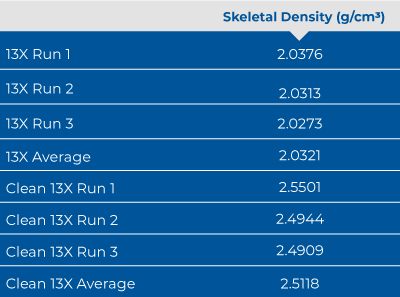
The average skeletal density value changed from 2.0321g/cm3 to 2.5118g/cm3 when pretreating 13X, a 23.6% change. Sample preparation might be a necessary step to obtain accurate results for porous materials when using a gas pycnometer.