The TriStar II’s Krypton Option can measure materials with surface areas as low as 0.001 m2/g and is ideal for difficult-to-measure pharmaceutical binders. Pharmaceutical binders such as micro-crystalline methylcellulose (MMC), lactose, and gelatin typically have surfaces areas under 2 m2/g and, therefore, are perfect candidates for krypton adsorption with the Tristar II analyzer.

Advantages of Using Krypton
Isotherms are collected by measuring the amount of gas adsorbed by a material over a range of pressures at a constant temperature. The quantity of gas adsorbed by a material is determined by taking the original quantity of gas dosed into a tube (Vi) and subtracting the amount of gas remaining in the tube after equilibrium is reached (Ve). For materials with low surface areas, the difference between the original amount of gas and the amount remaining after equilibrium (Vi – Ve) will be small and difficult to measure accurately, resulting in increased error. Normally for materials with low surface areas, the amount of material is maximized in order to increase this difference (Vi – Ve). Unfortunately, this approach has an upper limit depending on the size of the sample tube and the physical properties of the material. Another approach is to use an alternate analysis gas.
Krypton is an excellent choice for low surface area measurements. At 77K, nitrogen has a saturation pressure of 760 torr, whereas krypton has a saturation pressure of only 2.5 torr. Since pressure is proportional to the number of moles or molecules in a set volume*, there are ~ 300 molecules of nitrogen for every 1 molecule of krypton. When the quantity adsorbed is significantly small, lowering the amount of molecules present by a factor of 300 substantially reduces the amount of error.
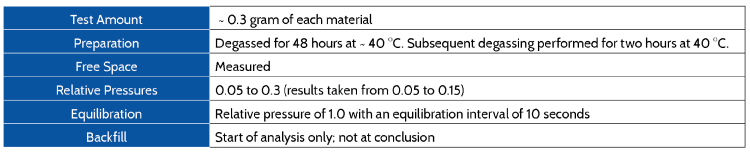
Analysis Parameters
USP method <846> Specific Surface is based on low temperature gas adsorption and the BET surface area calculation. The relative pressure (P/Po) range used for the isotherms for this testing was restricted to 0.05 < P/Po < 0.15. USP <846> also calls for a correlation coefficient (or goodness of fit) larger than 0.9975. All of the data presented meet this criteria.
*At liquid nitrogen temperatures, a non-ideality factor must be used for krypton.
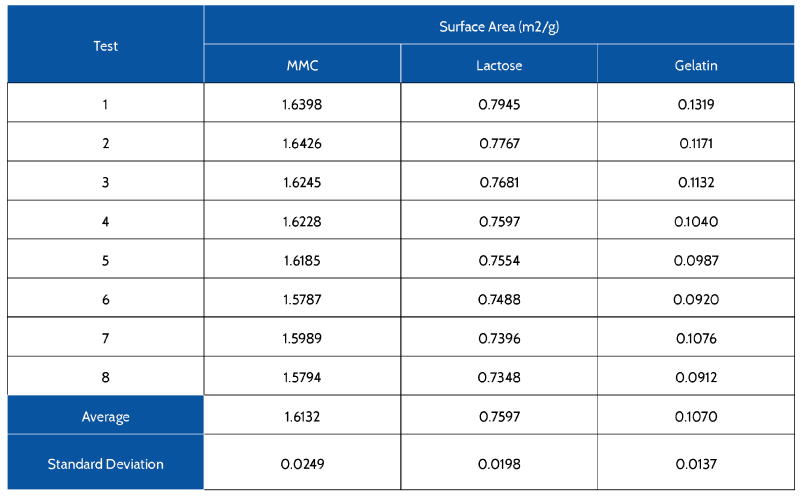
Analysis Results
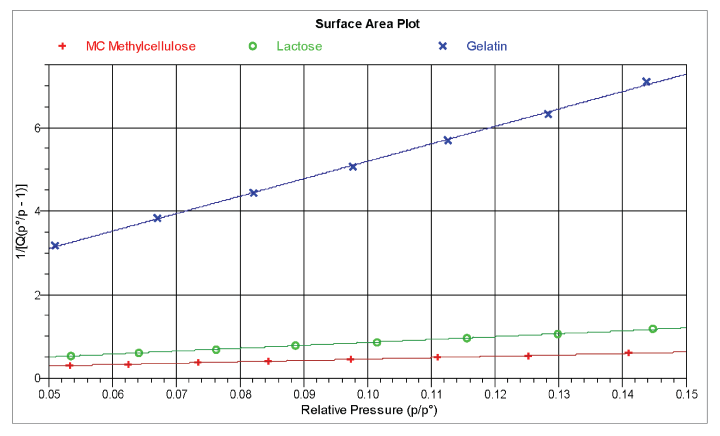
Surface area for the three samples was determined using the BET multipoint analysis. The results for all tests are shown below. Also shown are plotted isotherms for one of the tests.